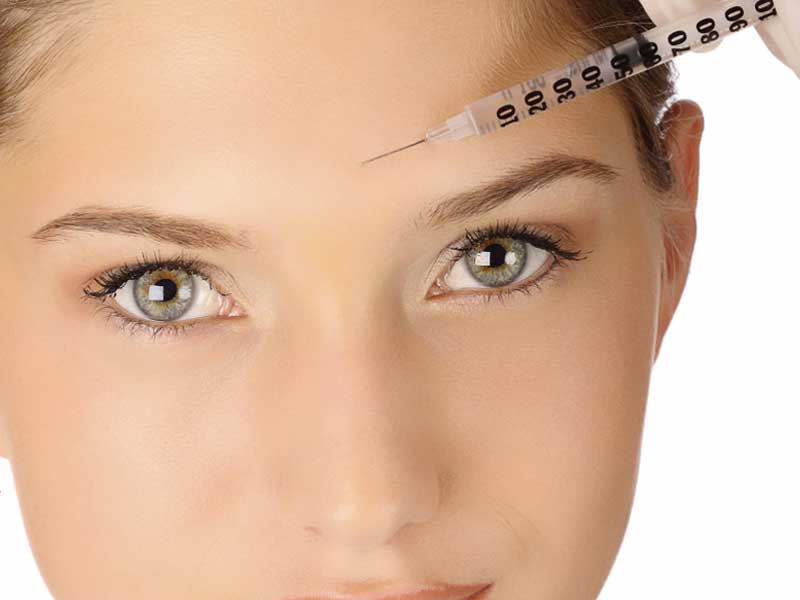
Lasik
LASIK is most similar to another surgical corrective procedure, photorefractive keratectomy (PRK), and both represent advances over radial keratotomy in the surgical treatment of refractive errors of vision. For patients with moderate to high myopia or thin corneas which cannot be treated with LASIK and PRK, the phakic intraocular lens is an alternative. As of 2011, over 11 million LASIK procedures had been performed in the United States and as of 2009 over 28 million have been performed worldwide.

Dry eyes
Some people experience dry eyes following surgery. Although it is usually temporary it can develop into dry eye syndrome. Underlying conditions with dry eye such as Sjögren's syndrome are considered contraindications to Lasik.
Treatments include artificial tears, prescription tears and punctal occlusion. Punctal occlusion is accomplished by placing a collagen plug in the tear duct, which normally drains fluid from the eye. Some patients complain of ongoing dry eye symptoms despite such treatments and dry eye symptoms may be permanent.
Dry eyes can usually be diagnosed by the symptoms alone. Tests can determine both the quantity and the quality of the tears.
Lagophthalmos
Blinking covers the eye with a thin layer of tear fluid, thereby promoting a moist environment necessary for the cells of the exterior part of the eye. The tears also flush out foreign bodies and wash them away. This is crucial to maintain lubrication and proper eye health. If this process is impaired, as in lagophthalmos, the eye can suffer abrasions and infections. Lagopthalmos leads to corneal drying and ulceration.
Treatment of lagopthalmos can include both supportive care methods as well as surgical. If unable to receive surgery, artificial tears should be administered at least four times a day to the cornea to preserve the tear film. Leading up to a surgery, a patient can undergo a tarsorrhaphy which partially sews the eye shut temporarily to further protect the cornea as the patient waits for care.
Halos
Some post-LASIK patients see halos and starbursts around bright lights at night At night, the pupil may dilate to be larger than the flap leading to the edge of the flap or stromal changes causing visual distortion of light that does not occur during the day when the pupil is smaller. The eyes can be examined for large pupils pre-operatively and the risk of this symptom assessed.
Complications due to LASIK have been classified as those that occur due to preoperative, intraoperative, early postoperative, or late postoperative sources: According to the UK National Health Service complications occur in fewer than 5% of cases.
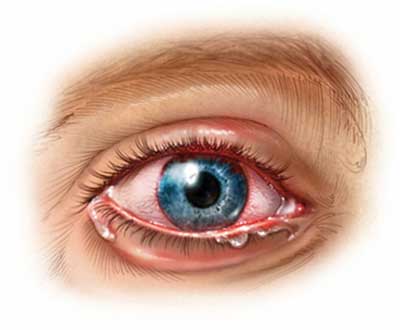
Uveitis
Uveitis is, broadly, inflammation of the uvea. The uvea consists of the middle, pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis requires an urgent referral and thorough examination by an optometrist or ophthalmologist and urgent treatment to control the inflammation. Prior to the twentieth century, uveitis was typically referred to in English as "ophthalmia.